Mobile App Designing is more crucial today than ever. The demand for intuitive and engaging app interfaces is getting out of control. As businesses race to capture user attention, the role of exceptional mobile app design becomes quite indispensable. From Mobile App Designing software to cutting-edge application design tools, the landscape is constantly evolving.
Why Does Mobile App Design Matter?
An interactive app design is not just a beautiful thing, it means there won't be hassles in its use. Research shows that 88% of users would not come back to a website if it has provided a bad experience. The same happens with mobile apps—when the design is lousy, user retention decreases drastically. That makes the ideal investment in best app designs a necessity for success.

User Retention
A recent survey, covering a subcategory of smartphone subscribers aged 13 years and older, indicated that 77% of users drop an app in the first three days after download. This proves well why a great user interface is important; a clear and attractive design will engage users from the very first touch point and keep them coming back for more.
Brand Image
Same UI for all uniformity instils trust and loyalty and reflects your identity and value for the users. Good app design enhances the user experience with charisma and builds up an image for your brand, making you outstanding among competitors.
Benefits of a Well-Designed Mobile App UI
Resource Conservation
A good and best app user interface design will ease development time by key user experience aspects, hence reducing redesigns, which are quite expensive, and allowing the developer to optimize resources.
Increased Customer Loyalty
Easy-to-use and intuitive UI will increase user engagement and retention, hence higher conversions and increased revenue. The satisfied user will likely become a loyal customer.
Improved ROI
Refine your App UI to improve conversion rates, elevating your ROI. A better user experience means increased user satisfaction and engagement levels.
Scalability
An intelligently designed UI will easily adapt to and scale with your app, so it still has a future when user needs and technologies change.
Improved Accessibility
Mobile App Designing an application with accessibility in mind makes it more usable by people with disabilities, hence opening its overall audience and making a positive statement for the developer's alleviation of social barriers.
16 Tips to Building an Effective Mobile App UI Design Process
Research and Understand Your Users
Knowing your audience is very critical. This will resonate with the users by collecting data and observing their behavioural patterns. Do online surveys, in-depth interviews, and usability testing to know the must-haves of users, their preferences, and pain areas. In addition, the use of analytic tools will trace a user's behavior and trends.
Use Well-Known Screens
Familiar screens decrease the learning curve and increase the comfort level. Incorporate very standard screens, such as logins, profiles, and settings, that users are familiar with. This also has an implication for consistency in screen layout and functionality: users will be able to navigate through your app intuitively due to experiences they have with other apps.
Decreases Clutter
Focus on primary elements and employ progressive disclosure so that options are shown only when they are needed. Avoid cluttering the device: Excessive information and too many features irritate the gadget. The approach keeps the interface clean and maintains high usability since it engages users to focus their attention on the parts that matter.
Delegate Tasks
Make things easier for users; if possible, break down complex tasks into simple and manageable steps, and, if possible, reuse data entered earlier in the process. Make use of autofill options or smart suggestions to minimize user effort; this reduces friction and makes the app more friendly toward the user.
Reduce User Load on Input
Make every reduction in typing possible by introducing autocomplete features; large, well-spaced buttons can make a huge difference. Hard-code as many dropdowns and checkboxes into forms as needed, with prefilled options which pre-populate the fields for faster data entry. This is more the case when it comes to mobile devices, where typing can be quite a labour.
Use Visual Weight to Express Importance
Contrasting with an importance ranking, mostly based on size, color, and contrast, show important elements more prominence. Emphasize major actions and critical information to attract attention in the eyes of users. This visual hierarchy will ensure that users easily locate and quickly engage with the major features.
Avoid Split-Screen
Make the flow seamless across screens and retain customers within the app to reduce abandonment. Design single-task screens that will help guide the user through a logical progression without distractions. This is the approach that will improve user engagement and satisfaction.
Ensure Design Consistency
It means an application-wide vision, functional, and external consistency. Related sections hold on to the same color schemes, Typography, and iconography. The elements used for interactivity should be consistent across the application parts. Keeping things uniform allows the users to develop a mental model of how an app works and hence properly use it.
Consider Screen Orientation
Design in portrait and landscape; ensure that high-frequency objects come to the top to make it easy for a single hand. Be sure that your app accommodates changes in screen orientation and size. This adaptability ensures an increase in usability and accessibility across different devices.
Filter App Features
Prioritize the main features and eliminate what isn't necessary to prevent overwhelming users. Consider only primary functionalities that deliver maximum value. A lean app certainly proves to be more engaging to users and serves their needs with a well-defined purpose.
Be Accessible
Make your application accessible to all users by incorporating colors that feature high contrast and intuitive navigation; the text should be legible, interactive elements should be reachable, and one ought to be able to navigate it using assistive technologies. Mobile App Designing for accessibility broadens the reach of your app and caters to a better experience for many users.
Reduce Push Notifications
Engage the user while still offloading them with many notifications. Give personal and timely, behavior-driven, and preference-driven notifications. Do not flood the users with too many notifications since they will leave or uninstall the app.
Usability Testing
Conduct usability testing to document and fix any issues before your app's launch. Regular testing with real users will help in the detection of problems and areas for improvement before launch. Iterate based on the feedback to fine-tune the app so that it's able to meet users' needs and expectations. This is an ongoing process that continues after launch for maintenance and improving the user experience.
65% of consumers form an opinion about a brand based on the app experience.
48% of users get irritated using an app with a non-responsive design.
94% of all first impressions are related to design.
Designing Tools and Technologies For An App
There are numerous application design tools available in the market, with each one focusing on a unique feature of app designing. Here are a few of the commonly used tools:
Sketch
Sketch combines everything one would want to love in a vector-based design tool; simplicity and speed make it perfect for designing user interfaces.
Adobe XD
This is an all-rounded suite of design and prototyping tools supporting vector designs and wireframes, with repeat grids, responsive resizing, and seamless integrations with other apps from Adobe Creative Cloud.
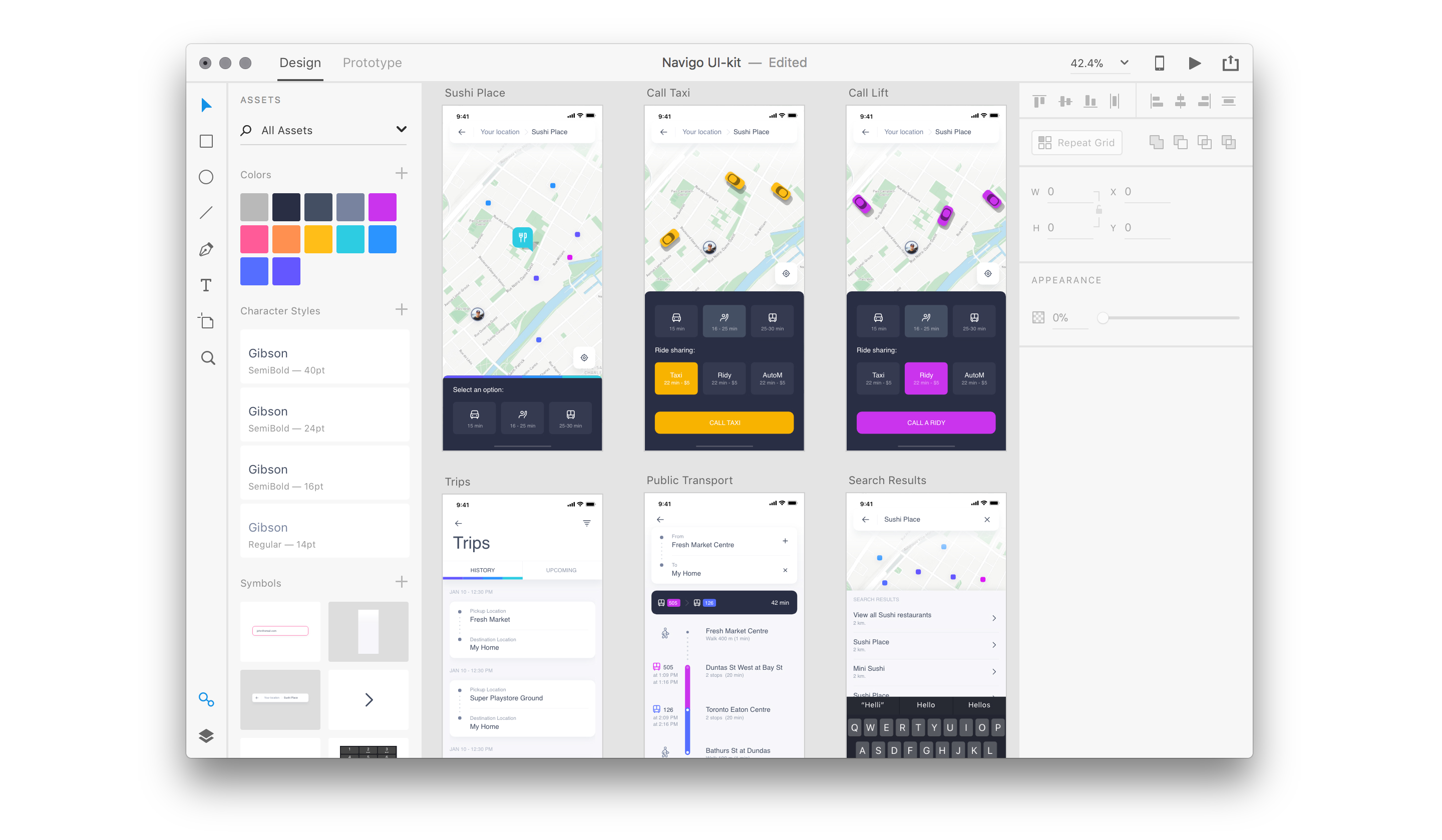
Figma
Figma is a cloud-based design tool; this is very powerful and one of the most appreciated collaboration features for design teams. It provides all basic designing features such as vector networks, prototyping, and version history, making the tool perfect for Mobile App Designing using UI/UX.
Axure RP
Axure RP is a detailed wireframing and interactive prototyping tool. Advanced conditional logic, dynamic content, adaptive views, etc., make it suitable for Mobile App Designing complex app interactions. Extensive usage of Axure RP is found in User Experience Design and User Testing.
Framer
Framer is an interactive-design-focused design tool. It has strong prototyping capabilities that let designers bring about realistic animations and interactions. Framer's code-based approach enables one to have flexibility and precision when designing app interfaces.
Principle
Principle is the animation and prototyping tool that permits users to effectively model interactions in high fidelity. It allows the designer to build quickly animated and UI elements that are interactive.
DXB APPS- Your Mobile App Development Partner In Dubai
DXB APPS is a leader in top-notch mobile app development dubai services. Specialized in application development dubai delivers comprehensive solutions that are tailored according to your business requirement. Be it innovative design or robust functionality; you can depend on DXB APPS for either of them.
Final Words
Designing an enthralling UI for a mobile app is the most challenging yet most rewarding task of a designer. If you put to work all the tips and tricks above, it would help you come up with an application that not only appeals to the users' eyes but also assures that the user shall stick around with the app. Getting professional services from an expert mobile app design company can enable you to emerge in the competitive market with an exemplary difference.
FAQs
1. What are the main features of a successful mobile app design?
Successful mobile application design involves user-centred design, intuitive navigation, and coherence in its design language.
2. Which ones are the core popularity tools in designing apps?
Popular ones are Sketch, Adobe XD, and Figma.
3. Why is mobile app design important for a business?
Mobile app design is important since it touches user retention and brand perception.